News Archive
Antibiotic resistance: Structures of a multidrug efflux pump in complex with antibiotics
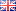
29 March 2012. A team led by Klaas Martinus Pos, CEF Investigator and Professor at the Institute of Biochemistry of the Goethe University Frankfurt, used X-ray crystallography to solve high resolution (1.9-2.25 Å) structures of the membrane protein AcrB in complex with multiple antibiotics. AcrB is the inner-membrane component of the major multidrug efflux transport machinery AcrAB-TolC from Escherichia coli. The study just published in the Proceedings of the National Acadamy of Sciences presents in one of the protein/drug complex structures the drug doxorubicin located in two monomers of trimeric AcrB; a dimeric doxorubicin sandwich bound to a pheripheral acces binding site in one monomer and a single doxorubicin molecule bound to a deeper binding pocket in the other monomer. The drug binding sites are exclusive for the respective conformational monomers and are separated by a switch-loop, most likely involved in a gating process mediating transport of the drug from the access site to the deep binding site. More...
Contact:
Klaas Martinus Pos
Institute of Biochemistry
Goethe University Frankfurt
Tel. +49 (69) 79829251
pos@em.uni-frankfurt.de
Full reference:
Eicher, T., Cha, H., Seeger, M.A., Brandstätter, L., Bohnert, J.A., Kern, W.V., Verrey, F., Grütter, M. G., Diederichs, K., Pos, K. M. (2012) Transport of drugs by the multidrug transporter AcrB involves an access and a deep binding pocket that are separated by a switch-loop. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci USA, Published online 26 March 2012. More.....